Network Manager
Overview
The NetworkManager is responsible for initializing bearers and selecting the appropriate one for external communications.
Configuration
The NetworkManager configuration parameters are listed under the item network in the ConfigStore:
- network.activate = true, enable / disable the NetworkManager. If activated, the NetworkManager will be automatically started.
- network.maxfailure = 2, if defined this value specifies the number max of failure before reboot on bearer selection (see Connecting state of figure 1).
- network.bearerpriority = {"GPRS", "ETH"}, list of available bearers ordered by priority. The NetworkManager will search, in this list, for the first appropriate bearer for external communications.
- network.maxconnectiontime = 300, *[OPTIONAL can be overridden per bearer]* maximum connection time for a bearer selected in the bearerpriority list if not the first of the list.
- network.retry = 5, [OPTIONAL can be overridden per bearer] number of retries before trying to connect to the next bearer in list.
- network.retryperiod = 10, [OPTIONAL can be overridden per bearer] number of seconds to wait before retrying to connect to a bearer
- network.smsfallback = "+33102345879", activate / deactivate (if nil) the sms fall back mode
- network.pinghost = "www.google.com", host for tcpping
- network.pingport = "www.google.com", port for tcpping
Other settings are bearer specific and in the general form of network.bearer.BEARERNAME.bearersetting
- network.bearer.GPRS ={apn = "some APN", username = "an optional username", password = "an optional password", retry='an optional retry', retryperiod='an optional retry period'}
- if no apn is define, the GPRSbearer behavior depends of the target.
- network.bearer.ETH = { mode= "dhcp", retry='an optional retry', retryperiod='an optional retry period'} }
- or network.bearer.ETH = {mode = "static", address = "10.0.0.189", netmask = "255.255.0.0", broadcast = "10.0.255.255", gateway= "10.0.0.254", nameserver1 = "10.6.0.224", nameserver2 = "10.6.0.225", retry='an optional retry', retryperiod='an optional retry period'} }
WARNING
If network.retry and network.retryperiod are not specified, specific bearer configuration is mandatory
Architecture
The NetworkManager is composed of two modules:
- NetworkManager, which holds all the connection logic, mainly initializing and selecting the appropriate bearer.
This module is the interface of the NetworkManager.
- Bearer, which represents and monitors a physical bearer, mainly mounting and unmounting a physical bearer.
This module is not intended to be used by a client.
Functionalities
The following diagram presents the initialization of the NetworkManager (network.activate = true).
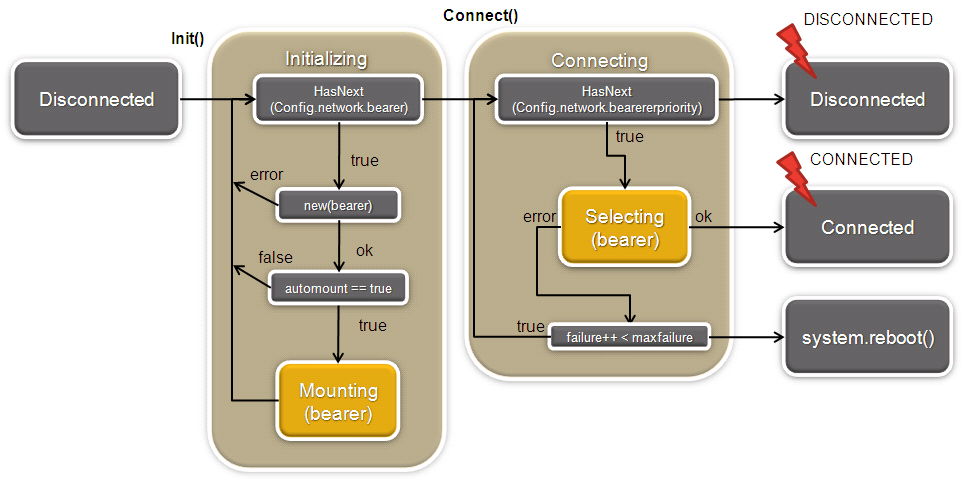
Figure 1: NetworkManager init()
- The NetworkManager is started in a disconnected state - When the Agent starts up, if ConfigStore parameter network.activate is true, the NetworkManager is required and the init() function is called - The init function initializes one at a time each bearer declared in the ConfigStore (network.bearer.BEARERNAME) - The connect function searches according to the network.bearerpriority list an available bearer for external communications. - If an appropriate bearer is found the NetworkManager emits the signal (CONNECTED), if not (DISCONNECTED). - The NetworkManager will trigger a reboot when the number of failure equals maxfailure (only if maxfailure is defined in the ConfigStore).
The NetworkManager allow to connect a specific bearer at anytime. The following diagram illustrates this feature.
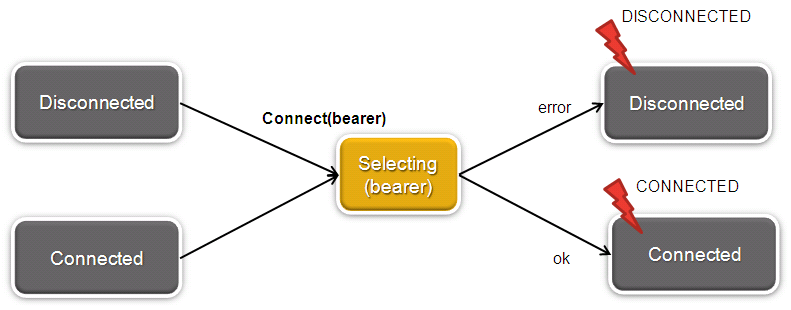
Figure 2: NetworkManager connect(bearer)
The Mounting and Selecting stages are describes and the two following diagrams
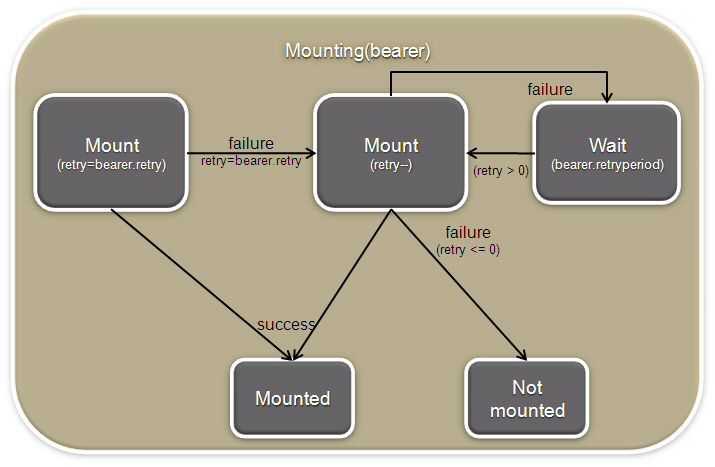
Figure 3: NetworkManager mount()
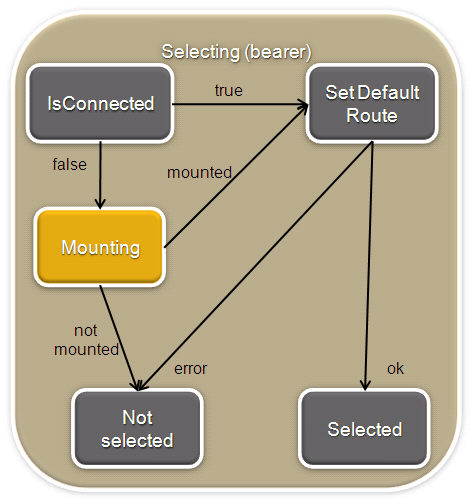
Figure 4: NetworkManager select()
Server connection
The NetworkManager first mission is to ensure connectivity for a communication action (i.e communication to the server).
The following figure illustrates the connection algorithm.
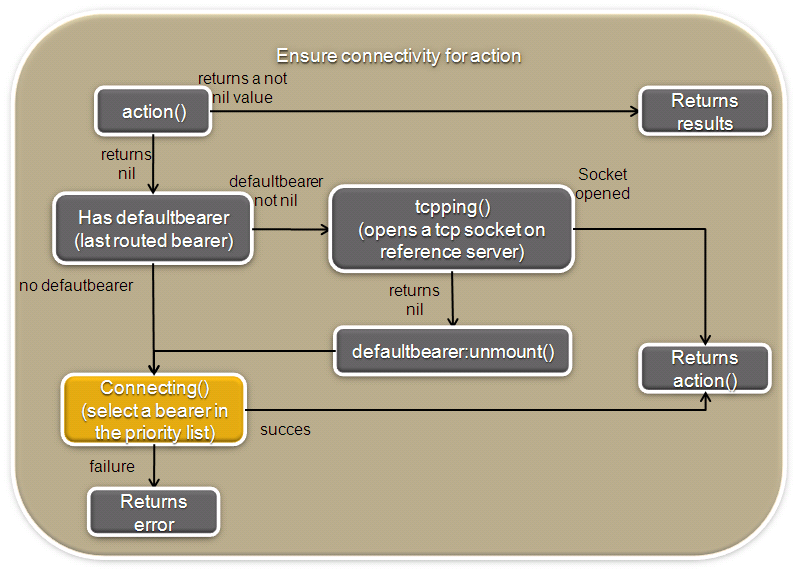
Figure 5: Ensure connectivity for a communication action
NetworkManager API
Functions calls
- init(), initializes the NetworkManager and all bearers.
- connect(nil or bearername, check_route), tries to connect to the given bearer (if bearername is specified) or tries to connect to a bearer from the network.bearerpriority list (selecting the first appropriate bearer).
If a connection is established the CONNECTED signal is raised (see events).
If check_route equals true, the selected bearer will be tested to see if a external communication is possible, In this case if the connection failed the DISCONNECTED signal is raised.
- getStatus(): return current bearer and current mode (auto or manual)
- tryConnectedAction(action, ...) returns action(...) results when the network is working and nil followed by an error on network error. I.E it returns the results of the function action() if its first result is non nil, otherwise try to verify/remount the network connection
Events
It raises specifics events on connection / deconnection:
- on connection => signal("netman", "CONNECTED", bearername)
- on disconnection => signal("netman", "DISCONNECTED")
where bearername can be GPRS, ETH...
All those events are raised with "netman" as emitter
Bearers API
Function calls
Bearers are instancied and initialized by the NetworkManager. They must provide following functions:
- new(bearername, automount), returns an new bearer instance of 'bearername' bearer. initparams is a table that will be given as parameter (key=value) when initializing the bearer shell script
If automount equals true, the bearer will be automatically mounted if disconnected.
- mount(), mounts the connection (unmount and mount)
- isconnected(), returns a boolean stating the connection status (false: not connected, true: connected)
Linux target specific bearer executables
In order to do the real work the bearer instance call an executable to mount/unmount the Linux network interface. The executable name is the bearer name: BEARERNAME, like: ETH or GPRS.
Those executables are meant to be target specific, while bearer instance logic must be related to embedded system only.
Those executables must use system status code and stdout to sent data to bearer instance within Agent.
As the only constraint is to be executable, those features can be done by a shell script (like those provided in Agent), or using any other language that produces linux executable.
WARNING
- Executables are to be put in bin directory in Agent runtime
- Executables must have correct access permissions.
- All parameters are given to executables using shell command line. Example: ./bin/ETH cmdname param1 param2 param3
- Output data are all mandatory (unless otherwise specified)
- Output data on stdout can be set to NULL value to specified that a data can not be retrieved. Example: in a shell script: echo "outputdata1" "NULL" "outputdata3", set data 2 to NULL.
The script take a "command" as first parameter. Depending on the command, more parameters may follow.
- init: initialize the network interface parameters.
- params: It takes as argument some specifics configuration like PIN number, GPRSAPN...
- stdout: the name of the corresponding Linux network interface
- exit status: 0 if bearer init was successful, a positive value in case of error
- start: mount the network interface (synchronous).
- params: the name of the linux interface to be mounted (returned by the init method)
- stdout: IP address, Hardware Address (MAC address), netmask, gateway (ip), dns1 (ip), dns2 (ip), ..., dnsn (ip)
- exit status: 0 if the network is mounted or a positive value in case of error
- stop: unmount the network interface (synchronous).
- params: the name of the linux interface to be mounted (returned by the init method)
- stdout: N.A.
- exit status: 0 if the network is unmounted or a positive value in case of error
- default: set the bearer as default route
- params: interface name, gateway address, dns address(es)
- stdout: N.A.
- exit status: 0 if the action is successful or a positive value in case of error
- stats: get dynamic statistics of the bearer
- params: interface name
- stdout: RX bytes, TX bytes
- exit status: 0 if the action is successful or a positive value in case of error




